06 Mar Whats Up – March 2020
Sun and Moon
The First Quarter Moon falls on the 2nd March at 21h57. The Full Moon occurs on the 9th March at 19h45 and the Last Quarter Moon falls on the 16th March at 11h54. The New Moon falls on the 24th March at 11h28.
On the 24th of March at 17h23, the Moon will be at apogee (furthest from Earth) at a distance of 406 700 km. The Moon will be at perigee (closest approach to Earth) at a distance of 357 100 km on the 10th of March at 08h33.
The March (Vernal) Equinox occurs on the 20th of March at 05h50 (local time), this marks one of the two dates in the year where day and night are approximately equal in length.
Planetary and Other Events – Morning and Evening
Venus still shines brightly in the Evening Star just after sunset. Mars, Jupiter and Saturn are located near stars of the constellation, Sagittarius. Mars, Jupiter and Pluto will be near the Moon on the 18th of March. Mercury can be seen from the middle of the month and it is near the Moon on the 21st of March.
Please do not miss out, on the 31st of March, Mars will be near Saturn,
Two meteor showers are active in March. The gamma-Normids are active from February the 25th to March the 22nd, peaking on the 13th of March. These showers are best viewed between 00:00 AM and 04:30 AM looking south-east towards the constellation Norma. Hourly rates are expected to be around 8 meteors per hour at the maximum. The delta-Pavonids are active from the 11th March to the 16th April peaking on the 6th April. They are best viewed between 02:00 AM and 04:30 AM looking towards the constellation of Pavo (the Peacock). Hourly rates are expected to be around 5 meteors per hour at the maximum.
The March (Vernal) Equinox occurs on the 20th of March at 23h58 (local time), this marks one of the two dates in the year where day and night are approximately equal in length.
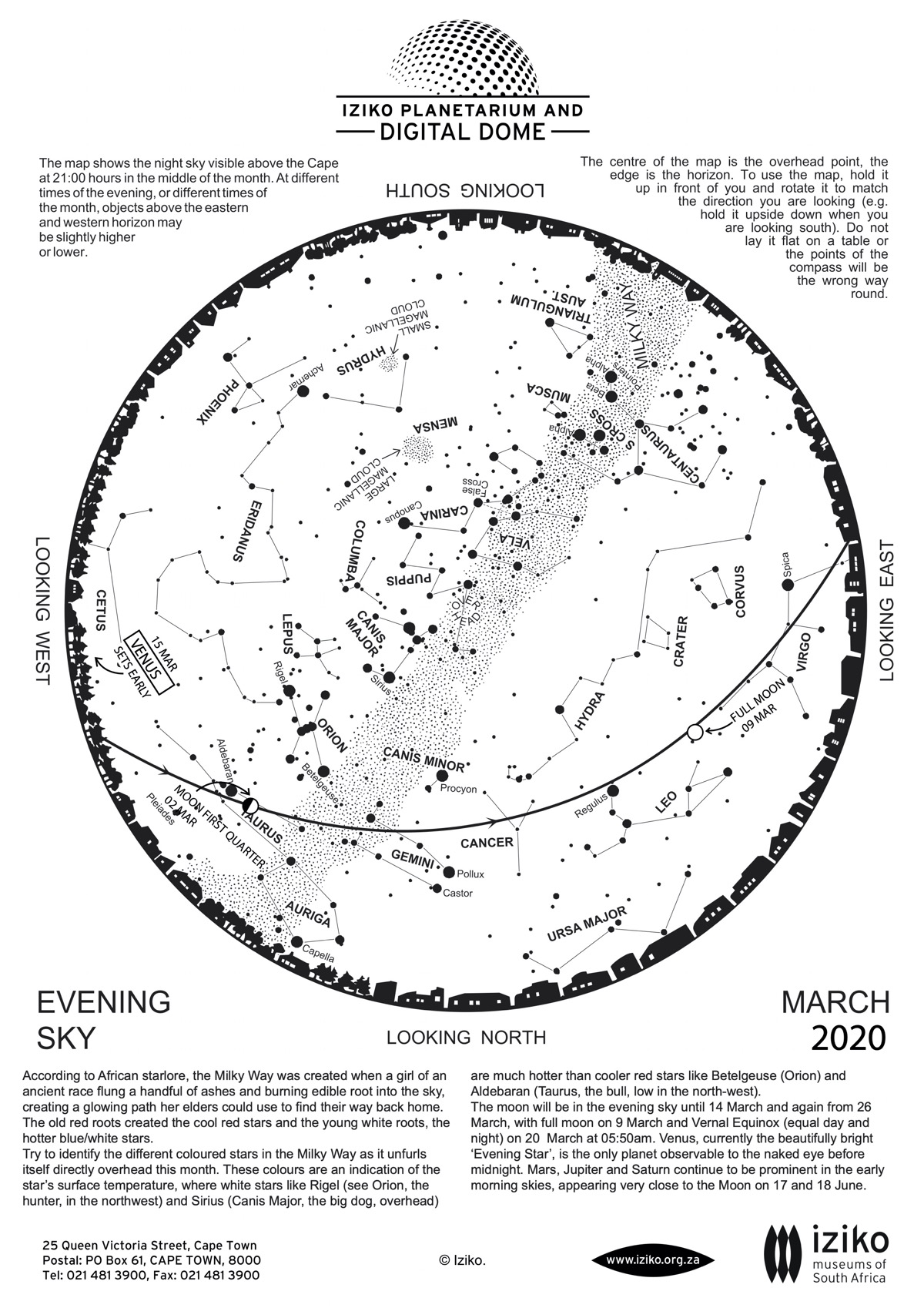
The Evening Sky Stars
The bright stars near the summer Milky Way continue to dominate the evening sky, just as in February. The Milky Way runs from NNW to SE in early evening at the beginning of March, and from NW to SE at the end of the month. If you live where a lack of city lights allows you to see the Milky Way, notice how very different the northern and southern portions appear. In the north the Milky Way appears relatively smooth and dim, becoming suddenly brighter and more clumpy south of straight up. In the north we’re looking out toward the edge of our Milky Way galaxy; while at the point where we see the sudden brightening (in the constellation of Carina, the Keel of the great ship Argo) we are looking along our spiral arm of the galaxy, where there are far more stars in the line of sight. Orion is still high in the NNW in early evening, outlined by the bright stars Rigel, Saif, Betelguese and Bellatrix. Taurus the Bull, with the brightish star Aldeberan, is low in the NW.
Directly below Orion in the north are the stars of Auriga the Charioteer, with brilliant Capella near the horizon. Capella is really a pair of giant stars which orbit each other every 104 days. About 100 million km apart, the two stars are each about 10 times the diameter of the Sun, and 50 and 80 times as bright, respectively.
Low in the NNE are the bright stars of the Twins, Castor and Pollux. Castor is another interesting multiple star. Through a telescope, there are 3 stars visible, and astronomers have discovered that each of these is itself double. Castor thus consists of 3 pairs of stars, with each pair of stars orbiting each other with periods of 20 hours to 9 days, the two bright pairs orbiting each other every 400 years, and the dim pair orbiting the other two over many thousands of years.
The brightest star in the sky (not counting planets), Sirius the Dog Star, appears almost overhead on March evenings, while a bit south of the point overhead is the second brightest star in the sky, Canopus. Rising in the southeast are the stars of the Southern Cross and the Pointers (Alpha and Beta Centauri). Alpha Centauri is a triple system, with two sun like stars orbiting each other every 80 years and a dim red dwarf tagging along at a much larger distance. This rather insignificant star was discovered by Robert Innes at the Union Observatory in Johannesburg in 1915, who also suggested the name Proxima. As seen from a planet around either of its brighter companions, Proxima would be an ordinary dimmish star, invisible for observers plagued by city lights. When it was discovered, Proxima was the faintest star known, but it has long lost even this distinction. At a little over 4 light years away, the stars of the Alpha Centauri system are the closest neighbours of our own Sun.
Achernar and the Magellanic Clouds (looking like detached pieces of the Milky Way) can still be seen in the southwest on March evenings. The Large and Small Clouds are the nearest galaxies to our own Milky Way (with the exception of two small galaxies actually being swallowed by our galaxy) and are about 180 thousand and 190 thousand light years away respectively. Compare this with Achernar, which is located inside the Milky Way and only a mere 90 light years away. The Sotho referred to Achernar as the senakane (the little horn) while the shield of the little horn is the Small Magellanic Cloud, known as mo’hora le tlala (plenty and famine). If dry dusty air made it appear dim, famine was to be expected.
The Morning Sky Stars
Bright orange Arcturus is low in the northwest before dawn, while ice-white Vega can be seen rising in the northeast. Vega is one of our neighbours, only 25 light years away, and is surrounded by a disk of dust which has intrigued astronomers. To the right of Arcturus is the dim semicircle of the Northern Crown, with the stars of Hercules between the Crown and Vega. Almost overhead is Antares, heart of the Scorpion. The Milky Way runs from northeast to southwest, with the brightest part of the Milky Way in the Scorpion and in Sagittarius the Archer.
High in the south are the stars of the Southern Cross and the Pointers, with bright Canopus very low in the southwest. Achernar shines low in the southeast, with the stars of the ‘Celestial Aviary’ above it. In this part of the sky are the Toucan, the Phoenix, the Crane and the Peacock, assorted scientific instruments and the Southern Fish.
Sivuyile Manxoyi 01 March 2020
Sivuyile@saao.ac.za

